Cure for Food Shortages Is Gene-Modified Bread, Tech CEO Says
Byand
-
Biotech leader says a Malthusian disaster could come soon
-
First GM wheat for consumer markets hangs on Brazil meeting
A world without enough food is just around the corner and can only be averted if humans forget their qualms about eating genetically-modified crops.
That’s according to Federico Trucco, the chief executive officer of Bioceres Crop Solutions Corp., a company that’s literally trying to put bread on the table with the controversial technology.
Bioceres is trying to succeed where no other company has before by selling genetically-modified wheat. While the vast majority of the world’s soybean and corn crops are already GMOs, these are fed to livestock. Biotech wheat, on the other hand, would be directly eaten by humans in bread and pasta, something consumers and regulators have roundly rejected in the past. Currently, only Argentina, where Bioceres is based, has ever approved a GM wheat.
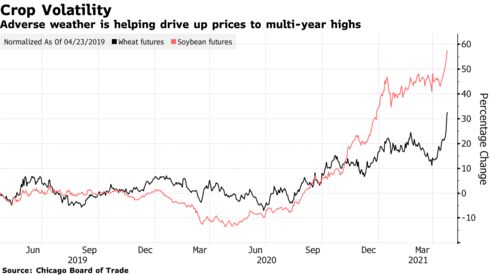
Trucco’s Malthusian warning about future food shortages comes as world leaders meet to recommit to emissions goals at time when climate change is decimating harvests, and a surge in food prices is forcing more people to go hungry.
“It’s going to get to a point when it becomes exponential and all of a sudden we need to change things yesterday,” Trucco said in an interview. “And I feel that’s coming up fairly soon. We’re not talking beyond five years.”
Other companies including Monsanto Co., before its merger with Bayer AG, have reversed course on GM wheat because of strong backlash, and Bioceres is still swimming against a tide of hesitant regulators and scared consumers.
Nevertheless, a milestone may come in just a matter of weeks with regulators in Brazil, a major importer, set to meet next month. If Brazil approves Bioceres’s wheat, the company would be able to start selling into its first market.
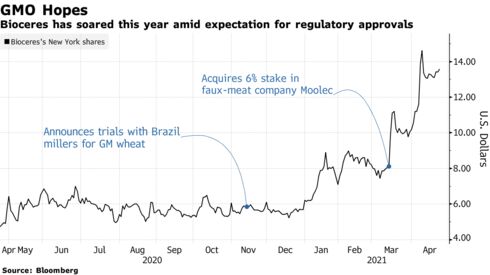
Shares rose by as much as 4.1% to $14.13 on Monday.
Trucco, a descendant of immigrant Italian farmers with a crop science doctorate from the University of Illinois, has described the task of getting GM wheat accepted as “monumental.”
Federico Trucco, chief executive officer of Argentine biotech company Bioceres, says policymakers and regulators need to quickly approve a new generation of genetically-modified crops, as climate change jeopardizes farm production and triggers an uptick in food prices.
For nearly two decades Bioceres — listed in New York and headquartered in Rosario, a river city that’s Argentina’s crop export hub — has been developing both genetically-modified wheat and soybeans to resist the droughts that are becoming more frequent from the Americas to Australasia. It’s also investing in a company that inserts animal genes into plants to increase protein content, a bet on the growing market for substitute meats.
A new generation of drought-resistant GM crops would help to put a floor under prices and mitigate the volatility of recent months, Trucco said.
From 2019: Drought-Stricken Wheat Belts Get Thorny Solution From Argentina
Bioceres is already in talks to convince millers and food manufacturers in Brazil to use its GM wheat strain as it also seeks clearance in other corners of the world, including the U.S., drought-racked Australia and Asia.
“If we can consolidate our position in Latin America and then persuade other geographies with their customers to join the monumental quest, we can have a staged approach to making this a reality,” Trucco said.
Sustainable Bond
Bioceres is preparing to sell up to $200 million in sustainability-linked bonds that would pay coupons tied to carbon capture on farms. Because Bioceres’s crops continue to photosynthesize in drier weather, they theoretically take in 6% to 7% more carbon dioxide than other plants.
“We’ve had a very good reception” from investors, Trucco said. “There is interest in trying to understand how GMOs can help in the face of climate change.”
Other highlights from the interview:
- The bond’s carbon capture goals start with 35,000 metric tons of CO2 by 2023 and an accumulated 156,000 tons in 2025. If Bioceres doesn’t meet the targets, the coupon rate would increase.
- Trucco is expecting key Chinese approval for Bioceres’s drought-tolerant soybean seeds in the second half of 2021, depending on results from field trials. Without clearance, the company would have to delay plans to roll out production in Argentina.
- Bioceres also needs to tweak the genetics of its soy technology for its next target markets of the northern U.S. and southern Canada.
- Speaking about Moolec, the alternative protein company in which Bioceres recently acquired a minority stake, Trucco said: “It’s not something we can pursue internally, because there’s only so many fights we can fight.”
— With assistance by James Attwood, Michael Hirtzer, and Carolina Millan